The Daily Observer London Desk: Reporter- John Furner
Quantum entanglement is a physical process through which pairs of particles become connected and remain so even when separated by vast distances. This fascinating phenomenon has been the focus of numerous research studies, due to its mysterious nature and promising real-world applications.
Ben Kain, a researcher at College of the Holy Cross, recently introduced a simulation-based model that outlines the possible connection between entangled particles and wormholes, hypothetical connections between distant regions in space-time. His model, presented in Physical Review Letters, is a concrete framework that could be used to test and study recent theories introduced by physicists Juan Maldacena and Leonard Susskind.
“In 2019 I studied something called Dirac stars,” Kain told Phys.org. “Fermions, which are described by the Dirac equation, when coupled to general relativity have star-like solutions in which the fermions can hold their configuration through their gravitational interaction. As a side note, traditional descriptions of stars, which of course are filled with fermions, do not fully account for general relativity.”
With the help of two undergraduate students at College of the Holy Cross, Kain previously wrote code that would allow him to simulate Dirac stars. A few years ago, other researchers discovered that when these Dirac systems include an electric charge, they could contain wormholes.
Wormholes are solutions to Einstein’s field equations of gravity, which can be visualized as tunnels with two ends located in distant places and/or at different points in time. Recent papers hinting that Dirac stars with electric charges have wormhole solutions assumed that the wormholes were traversable, meaning that particles could travel from one side to the other.
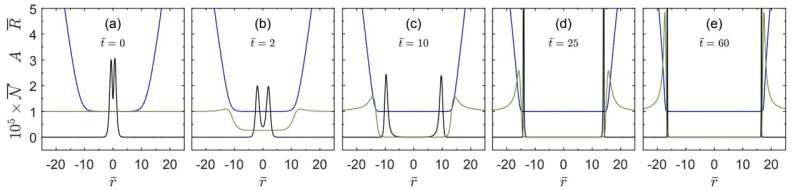
“I thought it would be very interesting if I could simulate this wormhole and confirm if the wormhole was traversable,” Kain said. “The Dirac system I focused on makes use of two fermions (i.e., two particles that obey the Pauli exclusion principle). My simulations require the system to be spherically symmetric, as this makes it easier to solve. To be spherically symmetric, the total angular momentum of the system must be zero. This ends up requiring the two fermions to be in a state called the ‘singlet state,’ which entangles the particles. ”
A decade or so ago, physicists Maldacena and Susskind introduced the idea that entangled particles are connected by wormholes. This is a bold and radical conjecture, as it offers a gravity-related explanation (i.e., wormholes) for a quantum mechanical phenomenon (i.e., entanglement).
“Entanglement requires faster-than-light communication, although this faster-than-light communication cannot be exploited by humans to send messages to one another faster than light,” Kain explained. “Maldacena and Susskind suggested that this faster-than-light communication might occur through a wormhole. They further suggested that the wormhole must be non-traversable (i.e., humans cannot travel through it) to be consistent with humans not being able to exploit the system for sending messages faster than light.”
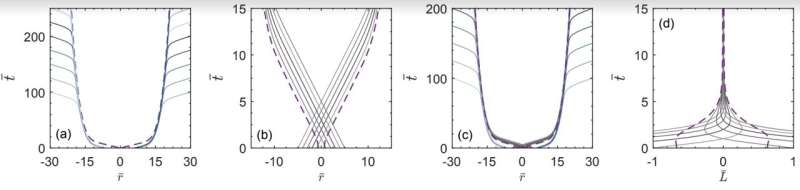
In his recent paper, Kain introduced a new model that could help to explore Maldacena and Susskind’s hypothesis. This model is based on the simulation of two entangled fermions connected by a wormhole.
When running this simulation, Kain found that in this scenario, black holes quickly form, covering both ends of the wormhole. These black holes ultimately make the wormhole non-traversable, meaning that nothing can pass through it and reach the other end.
“Since the model describes two entangled fermions connected by a non-traversable wormhole, it is a concrete model for studying Maldacena and Susskind’s conjecture,” Kain said. “They named their conjecture ER = EPR. ER stands for an Einstein-Rosen bridge, which was the first name for a wormhole. EPR stands for Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen, who were the first people to study entangled particles. The model I studied is thus a concrete example of ER = EPR.”
This recent paper introduces a new model to explore the possible connection between quantum entanglement and wormholes. Kain hopes that by examining his model further, researchers will be able to determine whether Maldacena and Susskind’s hypothesis is correct, while also determining how a wormhole could facilitate faster-than-light communication, which is a key requirement of entanglement.
“One idea I have for future works is to extend the simulations to allow matter to travel into one side of the wormhole, and hence into a black hole, and to travel across the wormhole,” Kain added. “I am interested in how this might affect the system.”